EGR 103/DAQ 2
This page contains pictures and graphs related to DAQ 2 for EGR 103. It has been updated for Spring, 2013.
Contents
Notes
Pauses
There are pause commands in the code which will cause the program to...pause - specifically when the program first runs to check the lights. You will need to hit a key to un-pause the program. The way to see if the program is paused is to look at the bottom left corner of your MATLAB window - it will tell you if it is paused.
Graph Labels
For this particular assignment, you do not need axis labels. You need a title on each subplot, however.
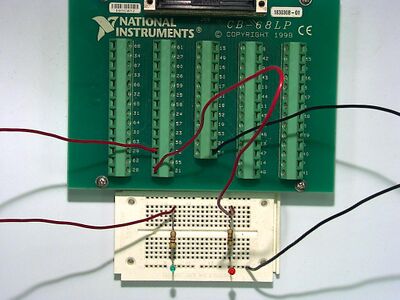
Circuit for BasicAOutput
Circuit layout for BasicAOutput.
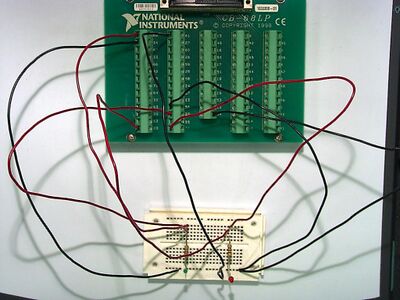
Circuit for BasicAIO
Circuit layout for BasicAIO (two measurements).
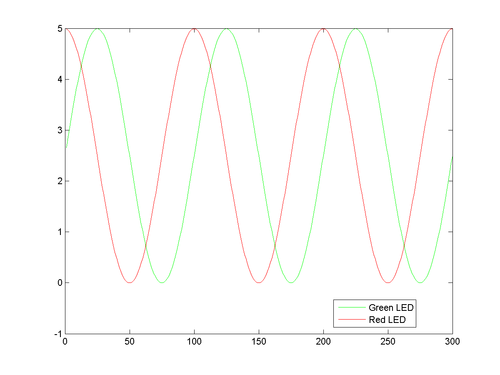
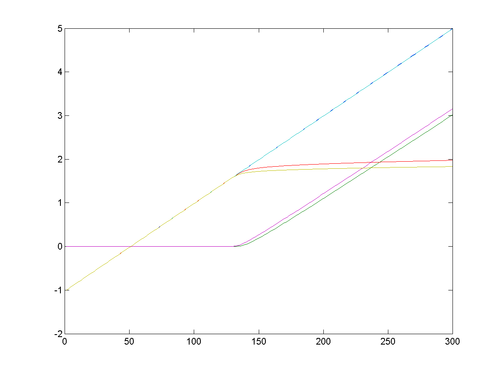
Graph from BasicAIO
Graph showing outputs when
Vout0 = 2.5+2.5*sin(2*pi*k/100);
Vout1 = 2.5+2.5*cos(2*pi*k/100);
That is,
\( \begin{align} V_{out,\,0}=2.5+2.5\sin\left(\frac{2\pi k}{100}\right)\\ V_{out,\,1}=2.5+2.5\cos\left(\frac{2\pi k}{100}\right) \end{align} \)
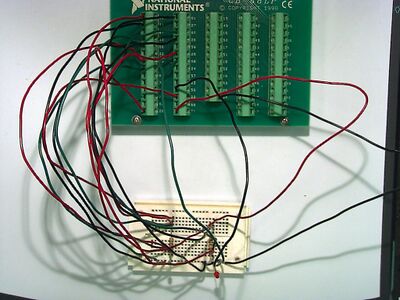
Circuit for AIO
Circuit layout for AIO (six measurements).
Graph from AIO
Graph showing outputs from six measurement channels.
Codes
Pasting codes from PDF files is...a bad idea. Here are the text versions of some of the codes in the assignment.
BasicAOutput.m
% Clear out workspace
clear
% Clear out DAQ objects
delete(daqfind)
% Create Analog Output Object
AO = analogoutput('nidaq', 'Dev1');
% Change sample rate
set(AO, 'SampleRate', 500);
% View Analog Output Object
AO
% Add channels to Analog Output Object
addchannel(AO, [0 1])
% Write values to output channels
putsample(AO, [5 5])
pause
putsample(AO, [0 0])
% Use loop to set several different voltages
for k=1:300
% Calculate voltages for each channel
Vout0 = 2.5+2.5*sin(2*pi*k/100);
Vout1 = 2.5+2.5*cos(2*pi*k/100);
% Put voltages to each output channel
putsample(AO, [Vout0 Vout1])
% leave line 31 blank for now
% leave line 32 blank for now
pause(0.02)
end
% Turn all outputs off
putsample(AO, [0 0])
BasicAIO.m
% Clear out workspace
clear
% Clear out DAQ objects
delete(daqfind)
% Create Analog Output Object
AO = analogoutput('nidaq', 'Dev1');
% Change sample rate
set(AO, 'SampleRate', 500);
% View Analog Output Object
AO
% Add channels to Analog Output Object
addchannel(AO, [0 1])
% Create Analog Input Object
AI = analoginput('nidaq', 'Dev1')
% Add channels to Analog Input Object
addchannel(AI, [0 4])
% Write values to output channels
putsample(AO, [5 5])
pause
putsample(AO, [0 0])
% Use loop to set several different voltages
for k=1:300
% Calculate voltages for each channel
Vout0 = 2.5+2.5*sin(2*pi*k/100);
Vout1 = 2.5+2.5*cos(2*pi*k/100);
% Put voltages to each output channel
putsample(AO, [Vout0 Vout1])
% Read voltages from all input channels
Voltages(k,:) = getsample(AI);
pause(0.02)
end
% Plot voltages versus index
n = 1:k;
Vleft = Voltages(:,1);
Vright = Voltages(:,2);
plot(n, Vleft, 'g', n, Vright, 'r')
legend('Green LED', 'Red LED', 0)
% Turn all outputs off
putsample(AO, [0 0])
Example Commands to Parse Data Set for Small Green and Red LEDs
load SmallData
SmallGreenTotal = SmallVoltages(:,1);
SmallGreenRes = SmallVoltages(:,2);
SmallGreenLED = SmallVoltages(:,3);
SmallRedTotal = SmallVoltages(:,4);
SmallRedRes = SmallVoltages(:,5);
SmallRedLED = SmallVoltages(:,6);
Subplot Structure for Plotting Code
The code below includes the commands for the small green LED assuming the variable names given in the code above.
subplot(3,2,1)
% small green plotting commands
plot(SmallGreenTotal, SmallGreenTotal, 'k-',...
SmallGreenTotal, SmallGreenRes, 'b-',...
SmallGreenTotal, SmallGreenLED, 'g-')
title('Small Green LED')
grid on
subplot(3,2,2)
% small red plotting commands
subplot(3,2,3)
% large green plotting commands
subplot(3,2,4)
% large red plotting commands
subplot(3,2,5)
% rect green plotting commands
subplot(3,2,6)
% rect red plotting commands
Questions
Post your questions by editing the discussion page of this article. Edit the page, then scroll to the bottom and add a question by putting in the characters *{{Q}}, followed by your question and finally your signature (with four tildes, i.e. ~~~~). Using the {{Q}} will automatically put the page in the category of pages with questions - other editors hoping to help out can then go to that category page to see where the questions are. See the page for Template:Q for details and examples.